Aydın et al. (2025), J. Membr. Sci.
Aydın, O. K., Erel-Göktepe, İ., and Çulfaz-Emecen, P. Z. (2025). Solvent-resistant membranes via layer-by-layer assembly of cellulose nanocrystals and poly (acrylic acid). Journal of Membrane Science, 124481. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2025.124481
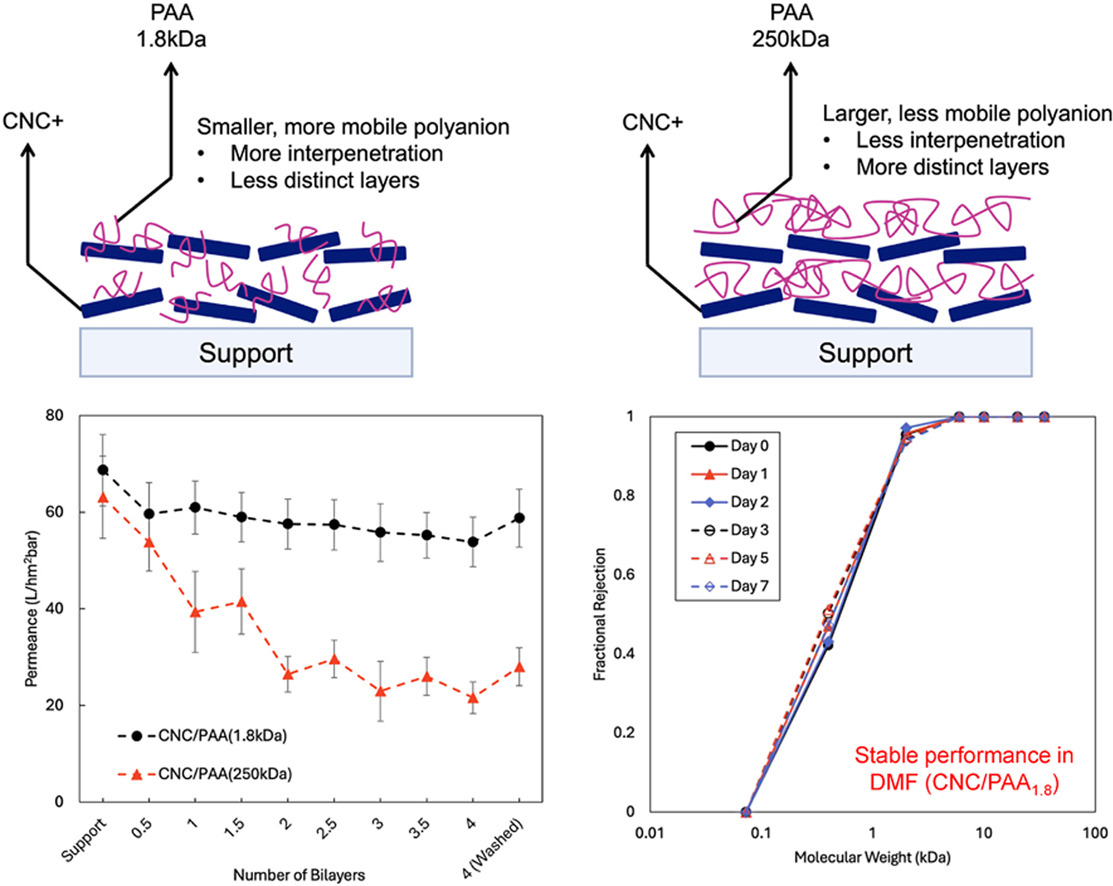
Layer-by-layer assembly of cationic cellulose nanocrystals (CNC+) with anionic cellulose nanocrystals (CNC−) and poly (acrylic acid) (PAA) with small (1.8 kDa) and large (250 kDa) molecular weight on phthalated cellulose and poly(ethersulfone) support membranes was demonstrated. All cellulose coatings made by CNC+/CNC− pair slightly decreased the molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) of the support, while using PAA as the polyanion and coating with applied transmembrane pressure over the support further reduced the MWCO. Using 250 kDa PAA, which is expected to be large enough not to penetrate through the voids in the CNC+ layer resulted in a significantly higher coating resistance and lowered permeance compared to the case of 1.8 kDa PAA, which would easily penetrate the CNC+ layer. The total layer thickness and the MWCO of CNC+/PAA membranes formed by the two different molecular weights on the other hand were similar, implying the CNC+ layer dominates the selectivity while a distinct PAA layer in the case of 250 kDa PAA increases the resistance. Both types of CNC+/PAA membranes were stable in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and dimethylformamide (DMF) up to a week, with MWCO ranging from 4.9 to 1.8 kDa and corresponding DMSO and DMF permeances of 6 and 11 L/hm2bar. PAA molecular weight did not affect the MWCO in DMSO while the membrane formed by CNC+/PAA (1.8 kDa) showed a markedly lower MWCO in DMF compared to the CNC+/PAA (250 kDa) membrane, implying that specific interactions between solvent and selective layer become important in determining the separation properties of the composite membranes.